Criteria for Success
- You feel confident in your movements and body posture.
- You maintain eye contact and forward-facing movements during the talk.
- You incorporate power poses when necessary.
- Your body movements flow naturally with your presentation and slides.
- Any movement that doesn’t support your main message is minimized.
Identify your purpose
A public presentation is more than just presenting information, it is also about engaging the audience and captivating their attention. If it wasn’t through our physical engagement, we might as well give the audience members an audio recording or slide deck instead. As a presenter, we attempt to liven the verbal messages with nonverbal gestures. Whether through body language, movement, or stage presence, these nonverbal components are just as important as the slides and talk you have practiced and prepared for. Incorporating conscious movements that serve to enhance how your message is perceived by your audience can help you:
- Engage your audience. Posture, gestures or movements, and your physical location on the stage are all factors that can be incorporated to create a story-telling effect that will keep your audience engaged throughout your presentation.
- Feel more confident. Strong body postures (e.g., power poses) convey confidence and a sense of importance during your talk.
Analyze your audience
Many audience members will arrive with the intention of learning more about your work and gaining some insight about your field. You can do more by also delivering an impactful and engaging talk that viewers can take home and remember. Audience types will dictate how you present yourself. For example, formal talks require formal attire, and this is also true in the types of nonverbal communication you can incorporate. Defined posture and deliberate movements are a must for professional talks, whereas more dynamic movements may be appealing for more casual and friendly presentations.
Similarly, the environment in which you are presenting will also determine your style. Poster presentations can be more informal with casual movements to guide the viewer. Department talks, on the other hand, should have movements that flow fluidly with your talk to guide the audience in your longer discussions.
Skills
Use eye contact to engage your audience
Possibly one of the most intimidating aspects of a talk is to look at the audience and to see their eyes gazing back at you. It is very common to escape eye contact by looking at your notes, the floor, or turning your back on your audience to face your slides. However, to be an effective presenter it is necessary to overcome these crutches in order to engage your audience. Making eye contact will help the audience feel important, like you are actually talking to them and not just giving a rehearsed speech.
If you already feel comfortable maintaining eye contact, remember to engage the entire audience. A few suggestions are:
- If it’s a large room, turn your head or even body to talk to all corners of the room, not just the people in the middle.
- Rather than just scanning the audience, can you take time to make one-on-one eye contact with individuals? Use this as an opportunity to gauge the audience’s level of interest. Seeing how they respond to your slides, transitions, etc. can help you adjust your talk as you go.
If making eye contact is challenging for you, here are two suggestions to help you work on this skill:
- Rather than trying to make eye contact with individuals, try looking at someone’s forehead, a colorful shirt, or the cushion of someone’s seat to create the illusion that you are making eye contact with the general audience. Alternatively, if picking out details is too distracting, you can look at or just above people’s heads to give the illusion of making eye contact.
- Once you feel comfortable looking into the audience, pick one or two places and go back and forth between these places during your talk to engage the entire room.
Emphasize deliberate movements and minimize unnecessary distractions (maximize signal-to-noise)
Here, we define signal as any movements that add substance to your talk and further engages the audience, such as conveying a message with your hands, or making eye contact with the audience.
Noise, on the other hand, is any unnecessary movements that distract the viewers, such as fidgeting or repetitive motions. Move with purpose. Do not ruffle your pockets or rock back and forth. Instead, present a straight, upright posture with arm movements that match the pace and flow of your talk. Adding purposeful movement to signify changes in ideas or to emphasize important points can add another layer of engagement to your talk. Some examples include:
- If you are comparing two concepts, physically weigh them out with your hands to convey the difference as if your hands were a scale.
- Casually walk to the other side of the stage when transitioning between ideas to physically cue the viewers that there is a change in topic.
- With a straight arm, point in the direction of the slide that has an important message. Make your movement distinct to indicate that the audience should focus on the slide, and not you.
Overall, this “art form” is unique to each person based on level of comfort and ability. We highly recommend using the Communication Lab to ask about how you can best utilize body movements to further enhance your talk. Alternatively, ask a friend for feedback, film yourself, or practice in front of a mirror to get a sense at what actions you naturally do during a talk, and reflect on how to change or enhance them.
(The metaphor of “signal-to-noise ratio” comes from Jean-luc Doumont’s book Trees, Maps, and Theorems.)
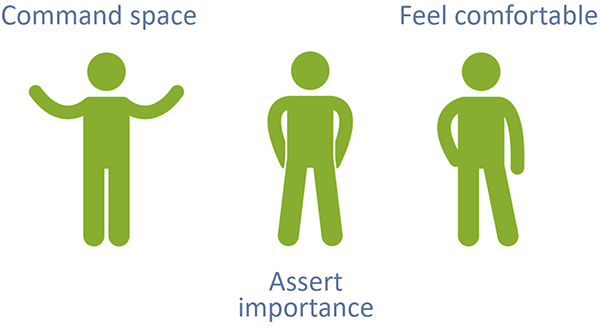
Use good posture and incorporate power poses
Many of us are rarely conscious of our posture, yet this is the first impression you will make to your audience even before you speak. A straight back and a level chin with your eyes facing the audience will show that you are prepared and ready.
Power poses can help assert confidence and importance during your talk. You are, in fact, the most important person in the room, so use power poses to make it look that way! What makes power poses distinct from low-power (or submissive) poses is the control of space. Hands on the side and a slightly wider stance command space on the stage and demands attention. Of course, overly dramatic, arrogant, or otherwise off-putting stances and posture should be avoided. Use a friend or video to find a power pose that makes you feel confident but doesn’t detract from your overall talk.
How to Practice
Non-verbal engagement is part of our daily lives, so pay attention to your movements when you interact with friends or co-workers. With practice, you will be able to naturally deliver a strong presentation when the time comes. Overall, things to consider are:
- Be conscious of your posture when standing and interacting with friends.
- Look people in the eye! Attempt to make eye contact with those you talk to.
- Pay attention to your small and fidget-like movements, even while by yourself. If these unwanted habits go unnoticed during everyday life, you can expect these habits to creep into your talk without you knowing.
Finally, make an appointment with the Comm Lab if you ever want to practice one-on-one or to discuss your concerns related to your non-verbal presentation style.
Additional Resources
- Common Challenges and Fixes for Verbal and Nonverbal Communication – An extensive reference table created by the BE Communication Lab
- “The Importance of Nonverbal Communication” – A quick read with fun statistics about the importance of nonverbal communication and additional concrete suggestions for improving your skills.
- “Your Body Language May Shape Who You Are” – A TED Talk on the effects of power poses and how to incorporate them into your daily life.
