The graduate school personal statement is your chance to show the graduate committee what it would be like to have you in the department. Would you contribute positively to the program, work well with others, and have the necessary skills to undertake important research? Convince them you are worth the investment and that you’re a good match for their program through a compelling story that’s based on your concrete experiences.
If you are in a hurry, you can also check out this short video for quick tips.
1. Before you start
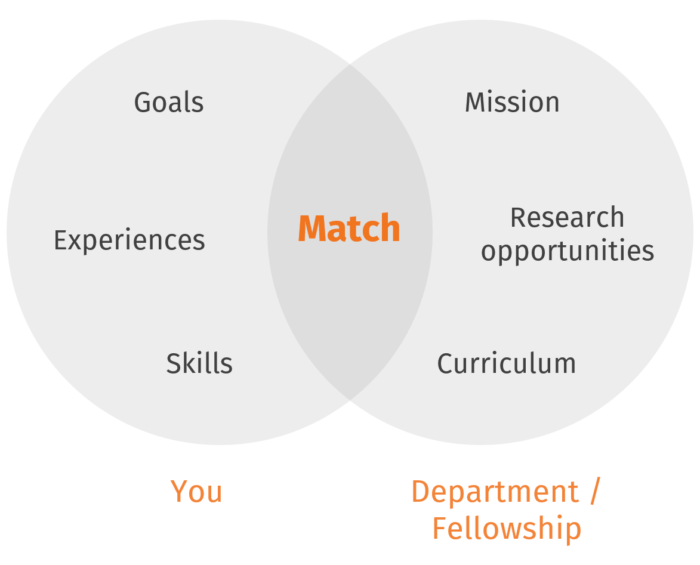 Most applications are rejected if they look generic or the applicant appears uninformed about the target program. Your strategy will be to demonstrate that you have the skills, knowledge, and background necessary to succeed in this particular department and that this program aligns with your goals. In other words, show that you are a qualified match.
Most applications are rejected if they look generic or the applicant appears uninformed about the target program. Your strategy will be to demonstrate that you have the skills, knowledge, and background necessary to succeed in this particular department and that this program aligns with your goals. In other words, show that you are a qualified match.
1.1. Reflect on your experiences and goals
Reflect on your experience, motivation, and research goals. What drives your research motivations, and how do your motivations link to your background and long-term goals?
Think beyond the technical space when brainstorming ideas for your personal statement. What do you care about and value—besides getting a higher-level degree? Include experiences that demonstrate your leadership, organization, and communication skills as well. Whether it’s growing up on a farm, mentoring high school students, or leading a robotics team, these experiences can be used to demonstrate motivation, commitment, and a good work ethic. These are attributes that can help you be successful in a research lab.
1.2. Do the research on your target program
To demonstrate how well you fit with the program, you must know what they value and what they are working toward. Each department has different goals and missions; some might value fundamental science, others engineering innovation, and others societal impact. Here are initial steps to take while researching a graduate program:
- Read the program’s website—specifically their mission statement. See what language they use to describe themselves, and echo that language in your personal statement. This is also a good place to see what kind of research is currently being performed. Looking at MIT NSE’s mission statement, what can we notice?

- Look up recent publications from your target research group (if you have one). The department’s website might not be up to date with any group’s new research directions. This will avoid the scenario where you express interest in working on a research project that has been abandoned.
- Get in contact with faculty in your target program. If you have had a positive discussion with someone at the department, describe how those interactions indicate that you will be a good match.
- State which professors in the program you would plan to work with and why their research interests you. Show how their research areas align with your background and your goals. You can even describe potential research directions or projects. This is even more effective if you have contacted the professor beforehand and spoken with them about the possibility of doing research for them. However, not naming a specific group of interest is not an automatic “reject.”
1.3. Consider your audience
A graduate committee will review your application and determine if you would make a successful graduate student in the department. Although the determination varies from committee to committee, the reviewers will be looking for the following criteria, which you should specifically address in your statement:
- Your ability to perform high-quality and independent research
- Your readiness to complete the expected coursework for your program
- Your likelihood to be a match in the department (ex: If you are currently in a physics program, you will need to explain why you’re seeking an advanced degree in nuclear engineering).
A graduate committee is usually composed of faculty from the program of interest—and may be the same people who will spend years working with you if you’re accepted. They more than likely have the following:
- A strong knowledge of the program’s general subject areas and familiarity with your proposed research area
- Familiarity with the academic setting and some courses, but not necessarily the courses you have taken
- Access to the rest of your application materials.
If applying to MIT’s Nuclear Science and Engineering department, you can assume your audience knows what a tokamak is, but you cannot expect (all of) them to know every component. Likewise, you need not list all of your courses but could emphasize one or two advanced subjects if they are relevant to your past and intended future research.
2. Structure of a personal statement
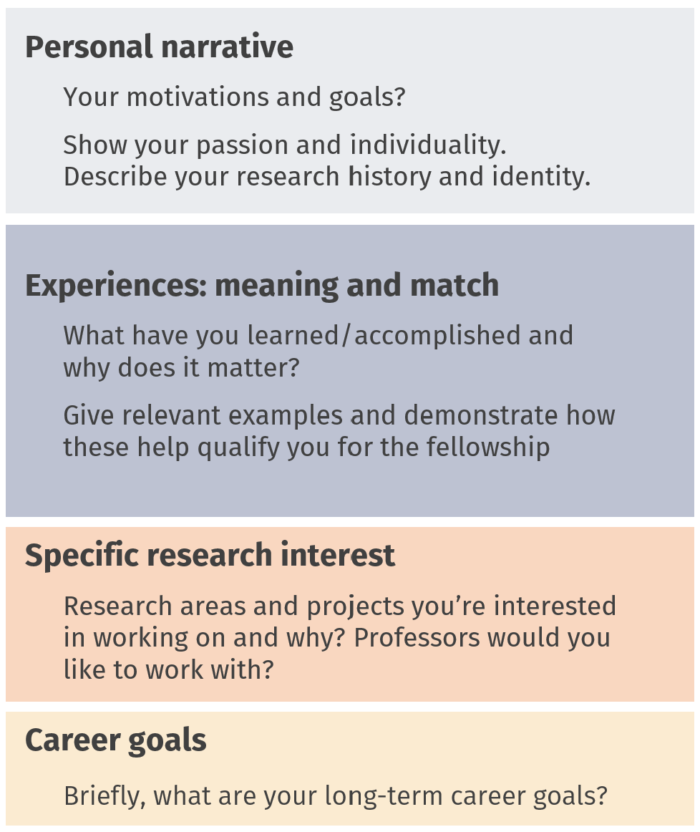
As long as you stay within the specifications set by your target program, you have the freedom to structure your personal statement as you wish. Still, you can use the structure shown on the right as a loose guide for demonstrating match.
2.1. Create a personal narrative
Build a personal narrative that ties together your personal history, experiences, and motivations. In addition to a few paragraphs (2-3) at the beginning of your statement, you can weave your motivation and goals throughout your document to create a cohesive story. This cements your identity into the minds of the graduate committee. If they remember you, they will be more likely to accept you!
When crafting a personal narrative, consider the following:
- What research directions are you passionate about, and why?
- Was there a moment that sparked your interest in your proposed field?
- What do you picture yourself doing in 10 years?
Keep these questions in mind as you are writing other sections of your personal statement.
2.2. Your Experiences
This section is typically 2-4 paragraphs long, with examples to illustrate your point. To decide which experiences to share, ask yourself these two questions: In which ways did this experience help me grow? Why should the review committee care? One common mistake is to describe an experience in great detail and then fail to translate it into relevant strengths that the committee would care about. Therefore, explicitly say what that experience means for your future goals, including your work as a graduate student.
2.3. Specific research interest
Spend 1-2 paragraphs describing your research goals. Briefly summarize the projects you want to work on (and professors you’d like to work with, if applicable), and how those fit in with your experiences. Describe how your past experiences have prepared you for working on this new project in graduate school. If you’re already in graduate school, you can spend more time on this section, as it is also a part of your past experiences.
2.4. Career goals
Finally, your long-term career goals should be a logical completion of the personal narrative you’ve built throughout the document, and usually takes up one paragraph. How will this graduate program fit into your future career? How will graduate school in general allow you to pursue these goals? Because your personal statement should show that you are a qualified match, describe how your goals overlap with those of the department or program. Your readers will not hold you to these goals, but they will see you are forward-thinking and have ambitions.
3. Maximize Effectiveness
3.1. Use concrete examples
Make your relevant experiences tangible by stating specific outcomes such as awards, discoveries, and publications. Whenever possible, try to quantify the experience. How many people were on your team? How many protocols did you develop? As a TA, how often did you meet with your students? Here are some examples of vague and concrete experiences:
| Vague experience (less effective) |
Concrete experience (more effective) |
| My mind was opened to the possibility of using different programming languages together to create code that is faster to run and easier to understand and modify. | During this project, I collaborated with other group members to develop a user-friendly Python wrapper for a 10,000-line Fortran library. |
| I won the physic department’s Laser Focus prize. | I won the physics department’s prize for the top student in my cohort of 20 students. |
| I learned about how particle accelerators work. | I took apart and repaired two electromagnetic steering filters inside of a particle accelerator. |
3.2. Explain the meaning of your experiences
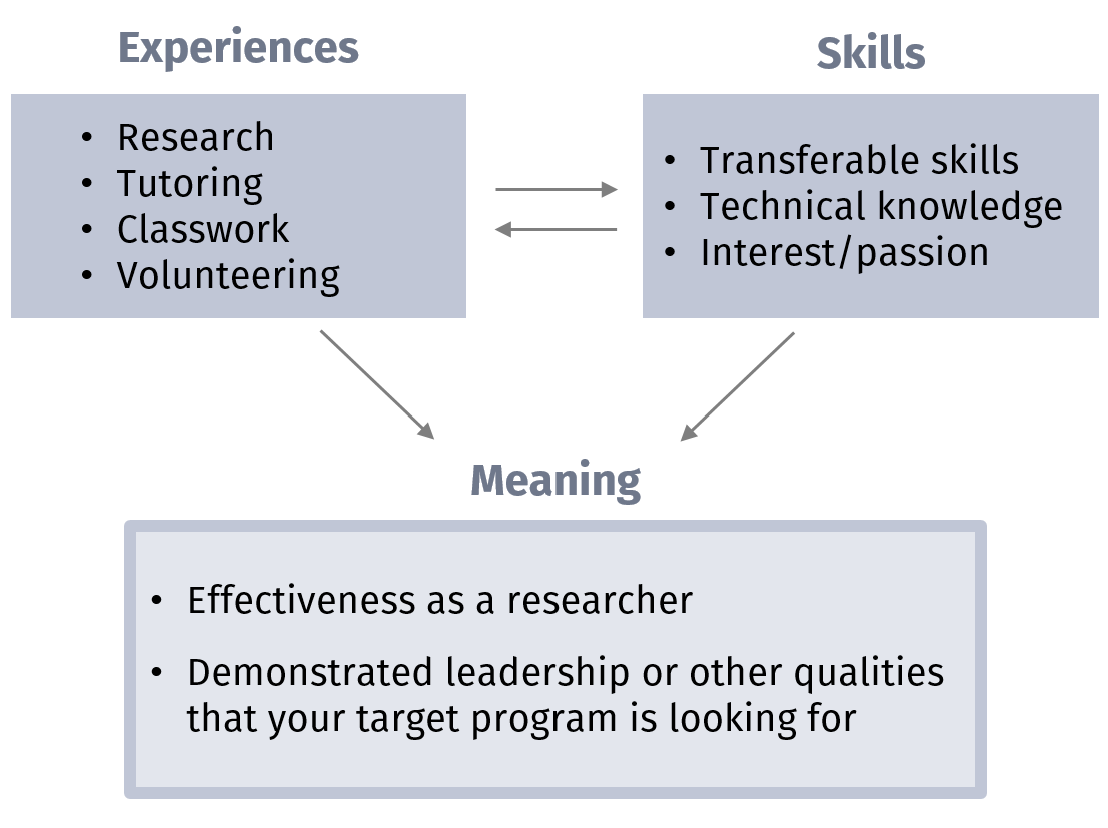 Your goal in sharing your experiences is to demonstrate that you have the qualifications, qualities, and drive needed to succeed in graduate school. Therefore, you will need to not only choose experiences wisely but also state specifically what they mean within the context of your application.
Your goal in sharing your experiences is to demonstrate that you have the qualifications, qualities, and drive needed to succeed in graduate school. Therefore, you will need to not only choose experiences wisely but also state specifically what they mean within the context of your application.
- Why was this experience important to your growth as a scientist?
- What did you gain from or demonstrate during that experience?
- How will this make you a better grad student?
Even if it feels obvious to you, you need to explicitly answer these questions to your audience. Here are some examples experiences that have been expanded to contain meaning:
| Experience only (less effective) |
Experience and Meaning (more effective) |
| “As a senior, I received an A in a graduate-level CFD course.” | “My advanced coursework demonstrates my ability to thrive in a challenging academic environment. A graduate-level computational fluid dynamics course challenged me to…” |
| “I independently developed a digital data acquisition software for gamma spectroscopy.” | “My research experiences have developed my problem-solving abilities. When the commercial software was insufficient for my gamma spectroscopy project, I … This has given me the confidence and software skills to attack open-ended research problems.” |
4. Quick Tips and Additional Resources
- Read the prompt carefully. Each school is unique, and will have unique requirements for their applications. If anything in those requirements contradicts with advice you read here or elsewhere, go with the application guidelines. Make sure your document meets criteria for length, formatting, font, file type, etc. specified in the application, and answers any specific questions asked.
- Double check your spelling and grammar. A well-written statement demonstrates your communication skills, which are essential for success in graduate school.
- Triple check that you have the right program and avoid accidentally putting the name of another graduate school into the document. Also check for specific labs or professors that you have mentioned in other statements. Using the search feature of your text editor will catch whatever you miss.
- Seek feedback from someone who’s not familiar with your work. Departments are diverse and your statement should make sense to someone in your field but outside your specific research area.
- Be strategic with letters of references. Do not go to professors who you think will write you the most positive letters. Instead, go to those who can write about specific experiences that demonstrates the skills that you want to highlight in your application. Each letter should bring new and complementing insights into who you are as a student and researcher.
- Check out other resources, such as The Key to Successful Applications (a blog post from MIT Graduate Admissions) and Apply to Grad School from MIT’s Career Development and Professional Development (CAPD).
5. Annotated Examples
Here are examples of graduate school personal statements from students who have been accepted into MIT NSE. Note that prompts vary from program to program, and sometimes from year to year within the same department. Be sure to follow the prompt for your program and your application cycle.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
To get started or receive feedback on your graduate school personal statement, make an appointment with one of us. We would love to help you!
